Comparative mapping

Among botanically related but distinct species, heterologous markers can be used for mapping. (A heterologous marker is one which has been derived from the sequence of one species, but is used for mapping in another.) These enable the construction of comparative maps which give a way of displaying species relationships.
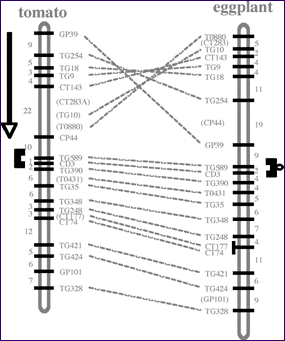 |
Here, tomato markers have been mapped in eggplant, highlighting a chromosomal inversion between the two species. Most grass genomes (e.g. maize, rice, wheat, barley, millet, etc.) are now inter-connected via such comparative genetic maps (see next 4 slides). |
While genome size varies dramatically among grass species, gene content and gene order are both typically well conserved.
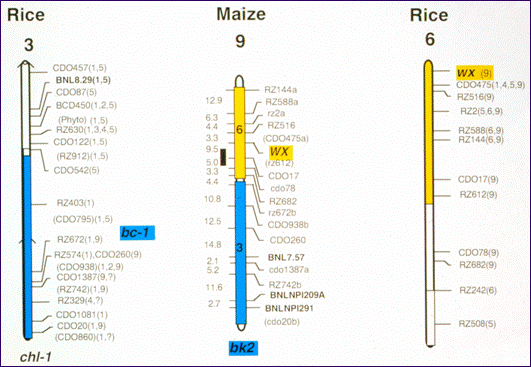 |
Note the use of common markers (RZ = rice marker, CDO = oat markers) across all three species.
(Based on Ahn & Tanksley 1993)
|





