

Nuclear vs plastid inheritance
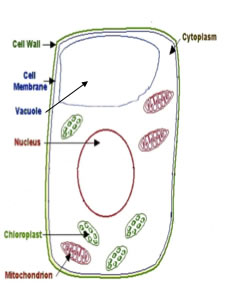 Most of a plant's DNA (nuclear DNA) is in the cell nucleus.
Most of a plant's DNA (nuclear DNA) is in the cell nucleus.
In the nuclear DNA, most genes are present as two copies, (except in polyploids where copy number is the same as the ploidy level)
Nuclear genes are inherited through both the male (pollen) and the female (egg) gametes.
Nuclear DNA enters the gametes after meiosis.

