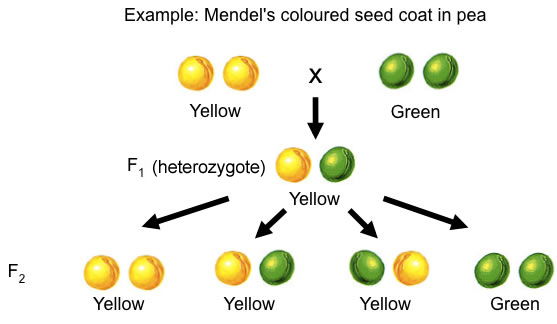
Dominance
At each gene in a diploid, there are two alleles, one inherited from the father, the other from the mother.
If these alleles are different from each other, the gene is heterozygous
If they are the same as each other, the gene is homozygous
Full dominance is where, In the heterozygote, only one allele (the dominant one)
is expressed, while the other allele (the recessive one) is silent.